What is Lymphosarcoma?
The clinical picture of lymphosarcoma is very polymorphic. In some cases, the first symptom of the disease is an increase in the lymph node (spleen) or testicle, the lobes of the thyroid gland, which have a dense consistency. In other cases, a pattern of poisoning, the appearance of autoimmune hemolytic anemia, capillary toxicosis, polyarthritis, eczema-like lesions on the skin may precede the detection of a tumor. The disease can also begin with the compression of the venous and lymphatic vessels with impaired organ function. Sarcomas, as well as lymphogranulomatosis, in rare cases produce aseptic necrosis of the affected tissues with the formation of fistulas.
Symptoms of Lymphosarcoma
The clinical picture of the disease does not have any specific features: a rapidly or slowly progressive increase in the tonsils, often at the beginning of one of them. Biopsy detects lymphosarcoma of the nodular or diffuse type. The tonsil lymphocytoma proceeds in exactly the same way: these tumors can be differentiated only on the basis of cytological and histological examination. Metastases to the lymph nodes of the neck do not serve as a contraindication to radiation therapy (15–25 Gy per total area) in the tonsil region — always both, even if only one is enlarged. In the future (2-3 months after the end of radiation therapy), it is advisable to spend 6 courses of COP. Remissions may be perennial.
Diagnosis by Lymphosarcoma
The blood picture has no specific features: red blood (with the exception of hemolysis and the spread of the process in the bone marrow) does not suffer, the number of leukocytes can be normal or slightly increased without significant changes in the formula. T-lymphoblastic sarcomas may be accompanied by eosinophilia in the blood and bone marrow. ESR may be normal or elevated. In cases of leukemization of lymphosarcoma, the blood picture resembles acute leukemia, which is determined by the suppression of normal hemopoiesis sprouts, blastosis in the blood and bone marrow. In some cases, lymphosarcoma has absolute lymphocytosis in the blood, and a high percentage of mature lymphocytes in the bone marrow.
Diagnostics
Hematosarcoma can be suspected in the case when a dense tumor appears somewhere that does not cause anxiety in the patient at first. An indication for a biopsy is such a tumor in the lymph node, on the skin, in the stomach, intestines, or tonsils. The absence of clinical signs speaks in favor of the tumor, rather than the inflammatory nature of the formation.
If you find a dense, painless lymph node after a catarrh that was transferred “on your feet”, for example, you should not rush to a biopsy: the doctor watches the patient for several weeks, sometimes taking antibiotic therapy, before deciding on a biopsy. Submandibular (about the angle of the lower jaw) lymph nodes, so often enlarged in chronic tonsillitis, are rarely the primary localization of hematosarcoma.
The clinical feature of Burkitt’s disease is the frequency of damage to the facial bones of the skull, especially the upper jaw and orbit. With the spread of the tumor often affects the organs of the abdominal cavity, kidneys, adrenal glands. In some cases, the process begins with them, and then has a worse prediction. In Burkitt’s lymphosarcoma, metastases to the nervous system are frequent, especially the spinal cord, less often there is a lesion of the cranial nerves. Only in 1% of cases peripheral lymph nodes are involved, the spleen is rarely enlarged. Burkitt’s lymphosarcoma is capable of leukemization.
The cells of this tumor are of blast type, often with vacuolization of the cytoplasm and even the nucleus, with basophilia of the narrow rim of the cytoplasm; Against their diffuse proliferation, non-tumor macrophages are located, giving the histological specimen a peculiar picture of the “starry sky”. Immunological typing revealed the B-cell nature of Burkitt’s lymphosarcoma.
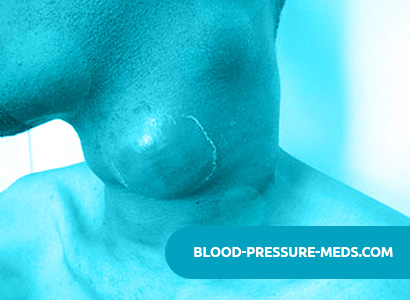
In lymphosarcoma of the peripheral lymph nodes, most often the primary tumor is found on the neck in the supraclavicular space. Metastases appear in the surrounding lymph nodes, a symmetrical neck, in the mediastinum.
Among lymphatic lymphoblastic lymph nodes, it is necessary to distinguish the pediatric variant with diffuse growth, rapid leukemization, metastasis to the central nervous system. For this reason, the diagnosis of lymphosarcoma of the lymph node in a child involves programmatic treatment according to the principles of treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children.
Lymphosarcoma of the thymus gland in children has a pronounced malignancy: the process quickly metastasizes to the lining of the brain and to the testicles; improvement, if it comes, is usually unstable. Histologically, this sarcoma is always diffuse; it comes from T cells.
Due to rapid metastasis, this sarcoma is often diagnosed already with a picture of acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the true origin of which is indicated by large tumor associations in the mediastinum, which are detected radiographically. Treatment should be carried out according to the program of treatment of acute lymphoblastic T-cell leukemia with mandatory irradiation of the primary lesion and metastasis to the substance of the brain, testicles.
The primary location of lymphosarcoma in the stomach (makes up 1-5% of stomach tumors) causes heaviness in the abdomen, pain after eating, sometimes gastrointestinal bleeding. The diagnosis is made using a biopsy (always with a biopsy imprint) during gastroscopy. Radiologically, such a tumor is usually indistinguishable from cancer.
Splenic lymphosarcoma is accompanied by an increase in the organ: heaviness appears in the left hypochondrium, a dense edge of the spleen is detected by palpation. Spleen puncture shows the predominance of blasts. Sometimes spleen lymphosarcoma causes the phenomenon of hypersplenism, in the blood decreases the level of leukocytes, platelets, less often erythrocytes. The rate of enlargement of the spleen is very different in different patients. There may be no change in the blood, although absolute lymphocytosis is sometimes observed, and Gumprecht’s shadows are possible. Bone marrow in spleen lymphosarcoma at the onset of the disease is usually normal, according to data and bone marrow puncture and trepanobiopsy. Splenic lymphosarcoma is diffuse and nodular.
In the latter case, well-defined aggregations of young lymphoid cells are noted — pseudofollicles, and there are no reproduction centers in them. There are also many young elements in the red pulp.
Radiation therapy should be considered the most rational method of treatment – close-focus X-ray irradiation or electron beam irradiation at a dose of about 40 Gy per focus.
Pulmonary lymphosarcoma with an isolated location is detected late. With a generalized lesion, the disease can trigger a kind of pneumonia: dry cough, increasing shortness of breath, high fever, “pale cyanosis”, light cyanosis of the lips. Antibiotic therapy at first can reduce the temperature, but the overall condition remains severe. Soon the temperature rises again to high numbers (39-40 ° C) and does not decrease. The general intoxication at the same time is expressed very moderately, the progressing respiratory insufficiency prevails.
Unlike pulmonary insufficiency of inflammatory origin, in patients with lymphosarcoma of the lung, the patients, choking, cannot assume a sitting position, they are forced to lie down. Radiologically common lymphosarcoma of the lungs resembles disseminated miliary tuberculosis. The diagnosis of pulmonary lymphosarcoma is made according to lung biopsy. At the autopsy, the affected lungs are so dense that they literally stand on a sectional table, not spreading out.
Histologically, there is diffuse proliferation of young lymphoid cells, contributing to the development of large proliferates infiltrating the interstitial lung tissue, alveolar septum.
When lymphosarcoma of the lung should be carried out courses of chemotherapy.
Tonsil lymphosarcoma deserves special attention because of the peculiarities of the tumor response to therapy.
Lymphosarcoma Treatment
Treatment of isolated gastric lymphosarcoma surgery.